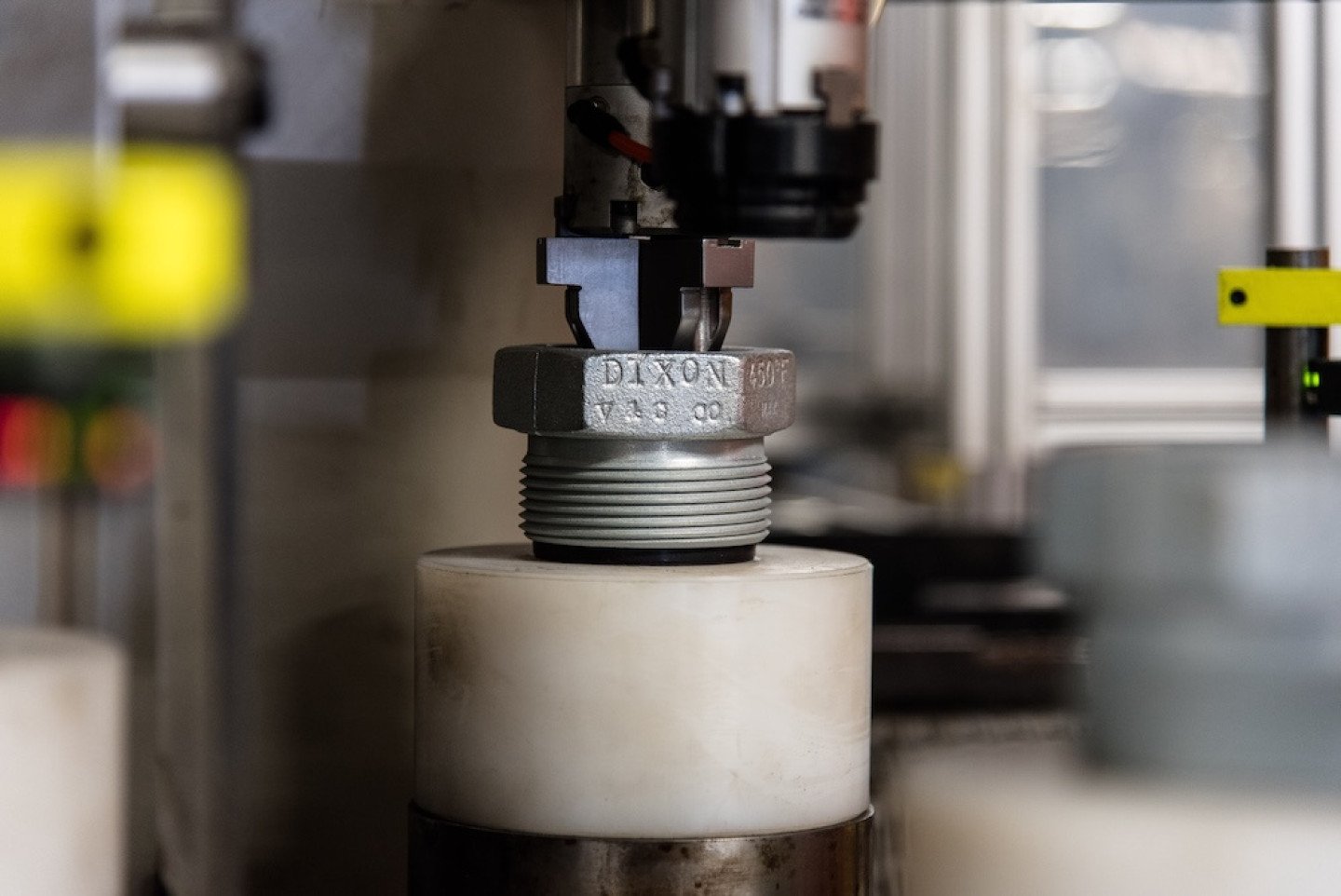
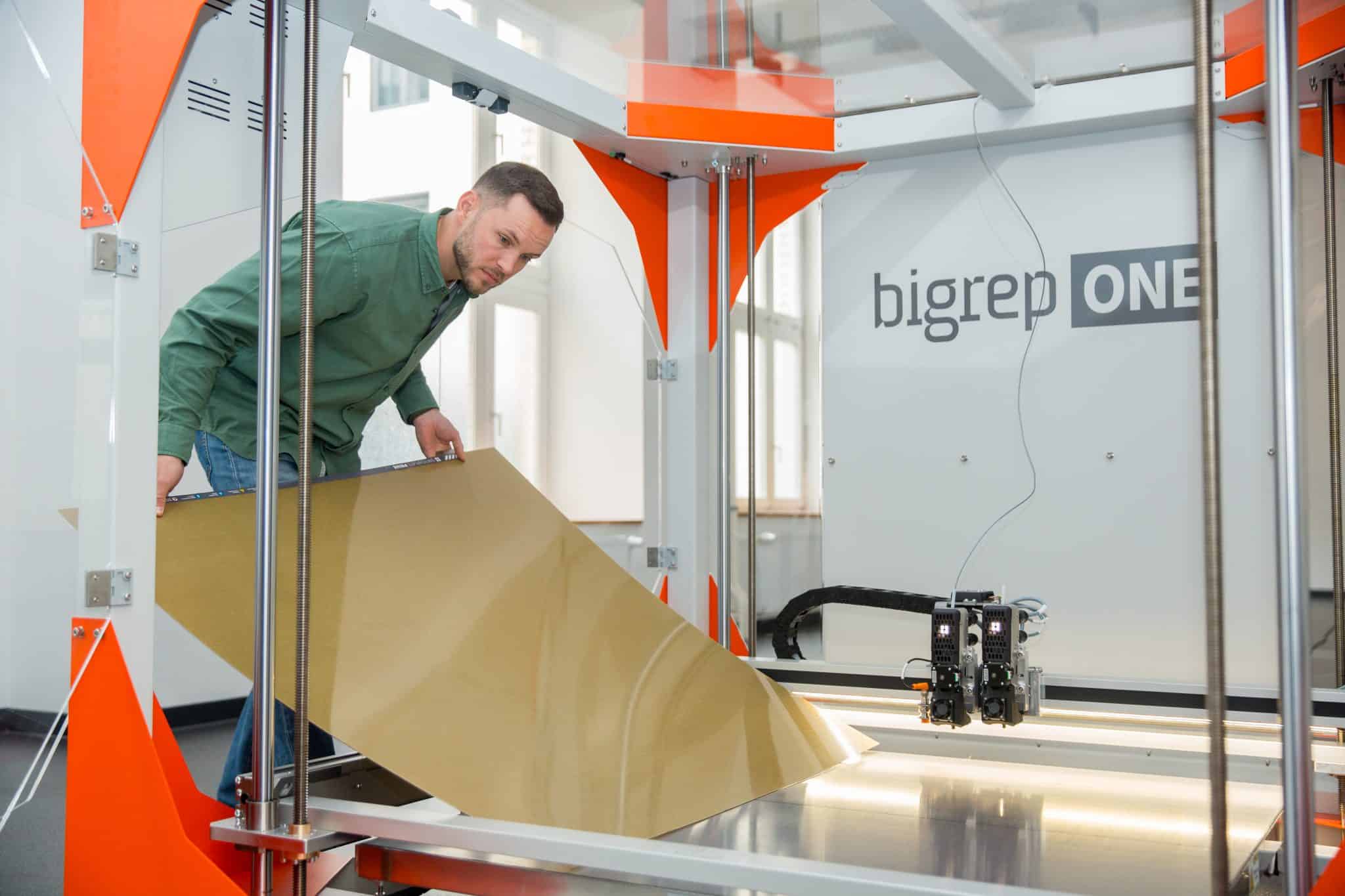
Metal parts manufacturing has undergone significant evolution over the past few decades. The transition from manual casting and forging to CNC machining and now to 3D printing represents a major shift in how metal parts are designed, produced, and delivered on the factory floor — transforming both the speed and flexibility of modern manufacturing.